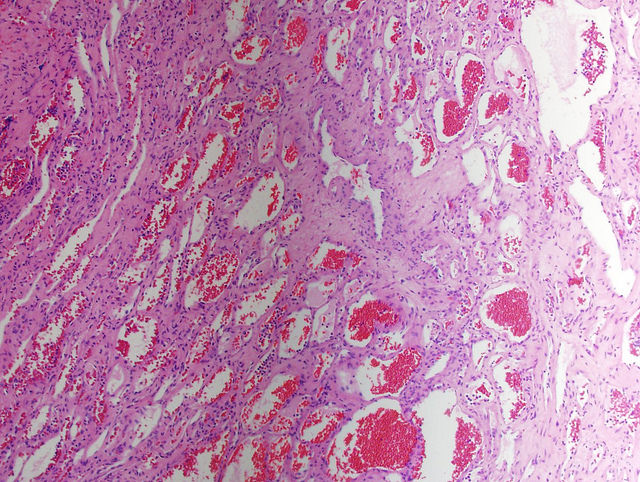
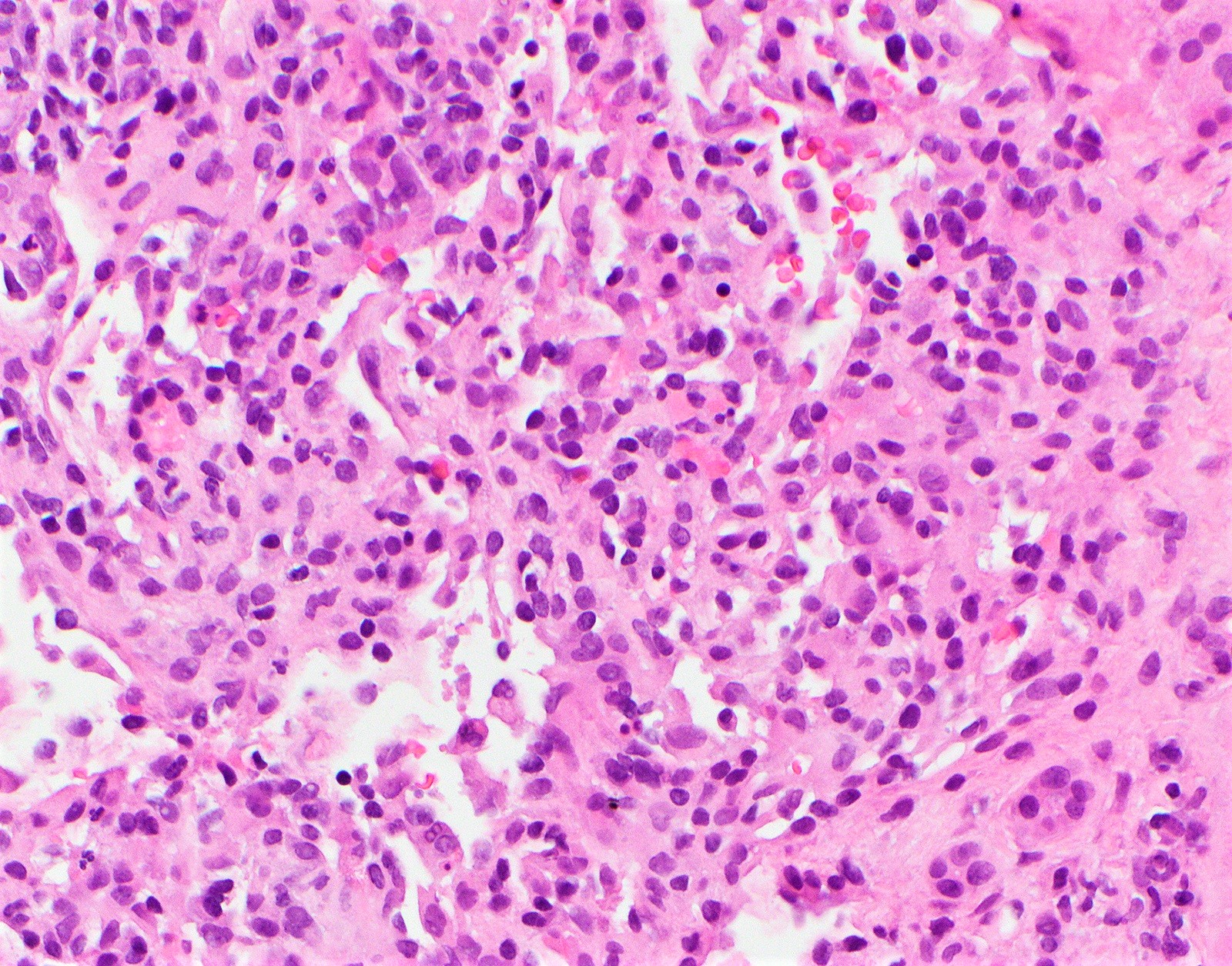
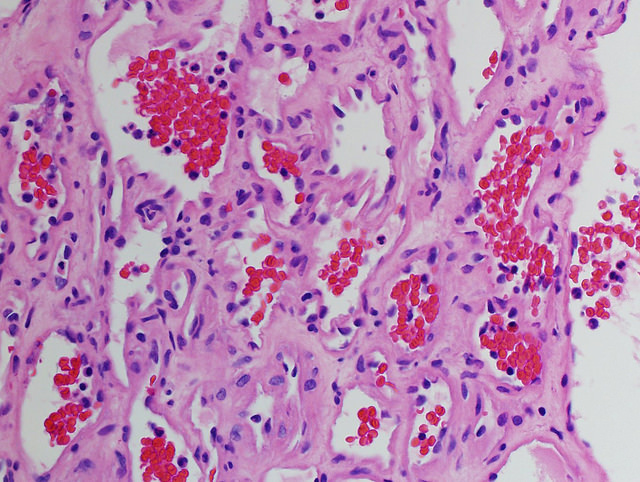
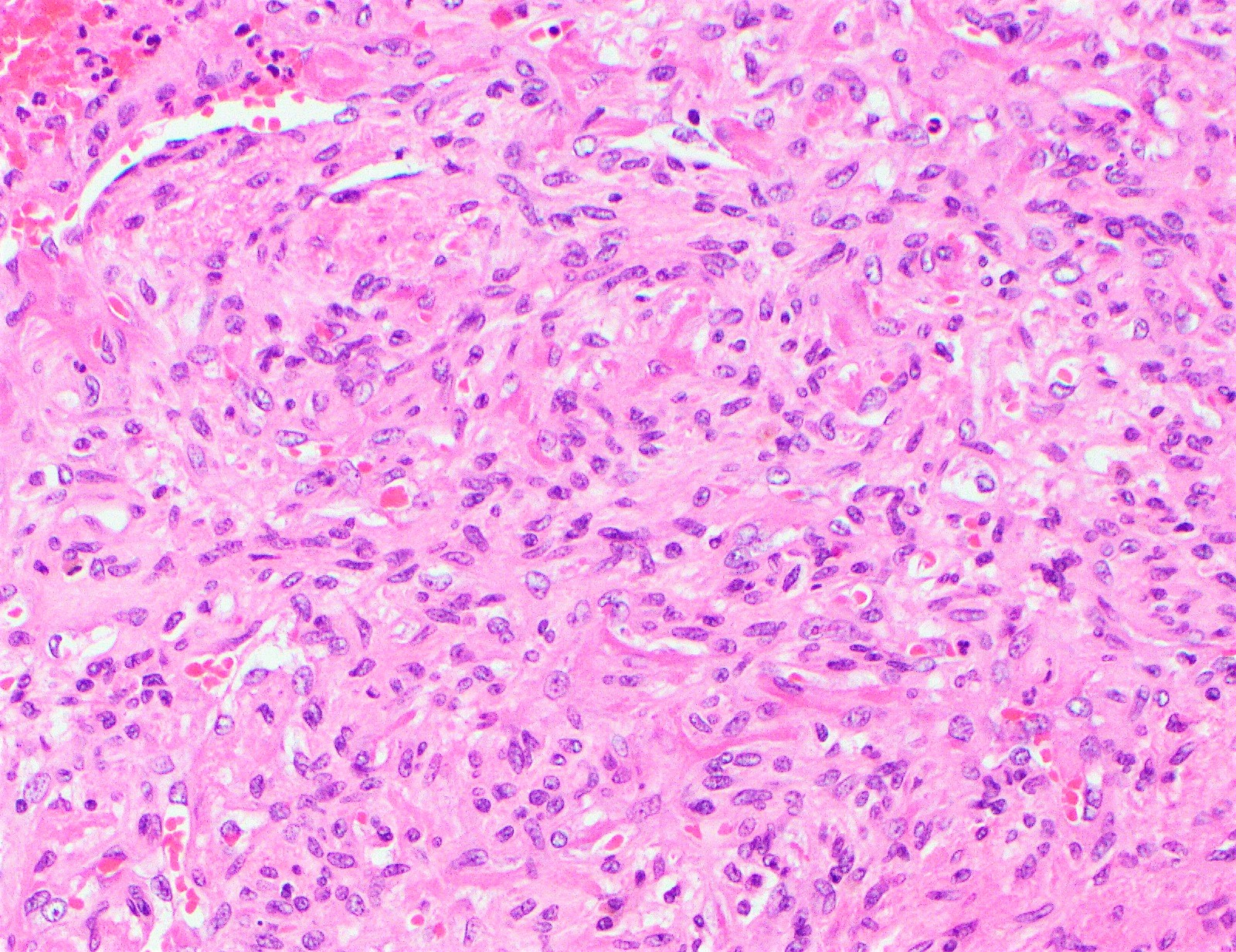
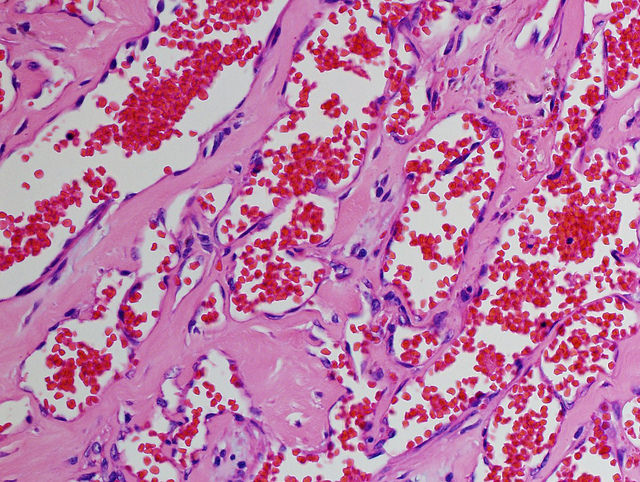
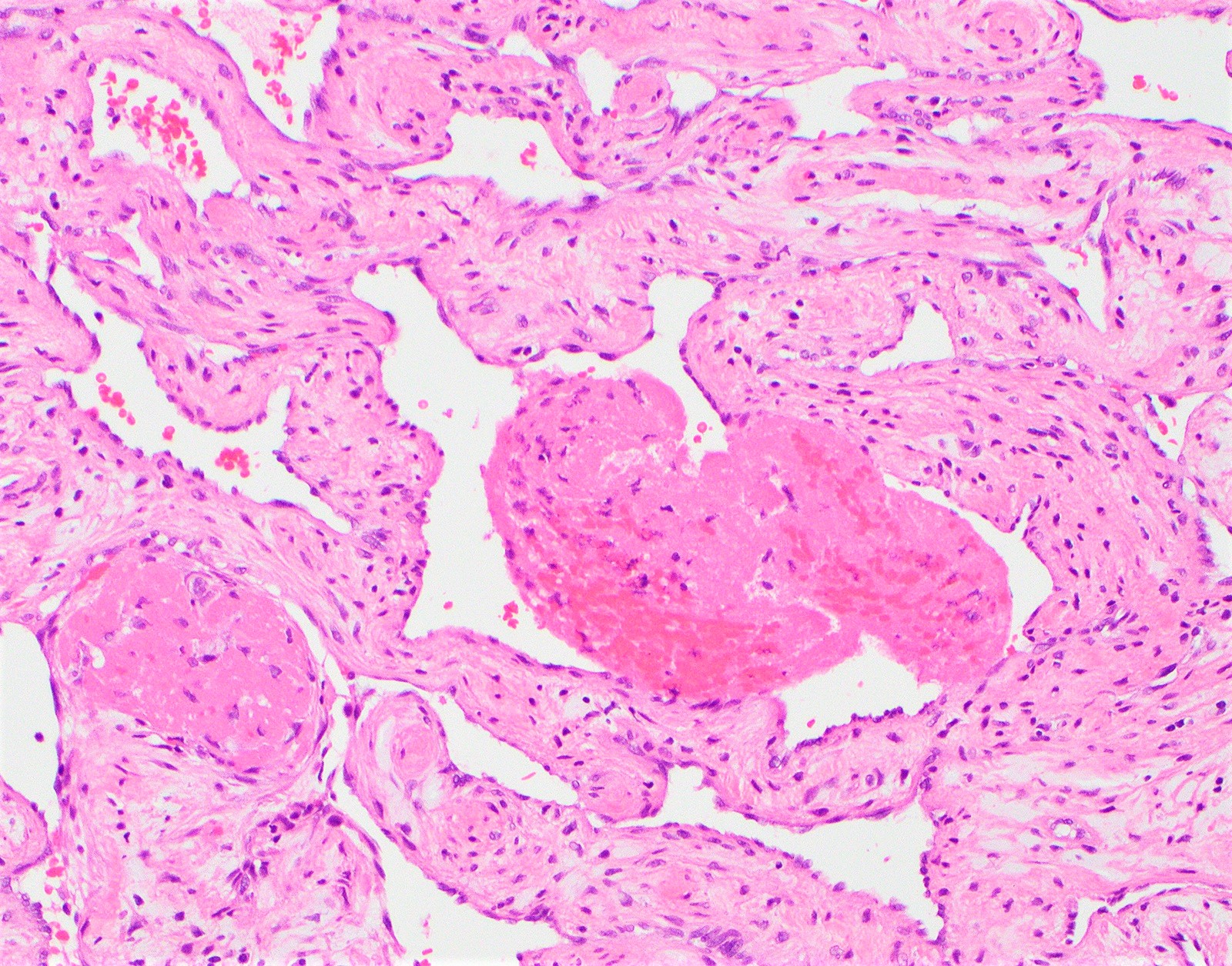
Types Of Hemangioma Pathology
Cystic or multilocular hemangiomas. Several types are seen in soft tissue.
Capillary Hemangioma Pathology Made Simple
Superficial on the surface of the skin deep under the skin and mixed.
Types of hemangioma pathology. Congenital or infantile hemangiomas develop at or near birth. A hemangioma is a common non-cancerous tumour made from blood vessels. A congenital hemangioma is present at birth and grows as a child grows.
Other articles where Hemangioma is discussed. Numerous dilated thin walled vascular channels of variable size lined by flattened endothelial. It is usually an incidental finding at autopsy but may present with abdominal pain.
There are different kinds of hemangiomas and the most common types are called capillary cavernous and lobular capillary. Hemangiomas with fluid-fluid levels. Congenital hemangiomas are fully grown when the baby is born but they do not grow after birth.
Before the year 2000 these lesions were grouped in with infantile hemangiomas. Tumours of the lids. Less frequent types are large heterogeneous hemangiomas.
Neoplasm vascular anomaly is divided into several disorders which one of them is hemangioma. Most hemangiomas occur on the surface of the skin or just beneath it. It is a benign non-cancerous growth.
A frequent type of atypical hepatic hemangioma is a lesion with an echoic border at ultrasonography. Hemangiomas may occur anywhere on the body. They are most often present at birth and tend to grow in the first few years of life sometimes contributing to obscuration of vision and amblyopia.
Cavernous and capillary Cavernous more common. Capillarycavernous lobular capillary cellular and epithelioid. Internal and external hemangiomas and hemangiomatous lesions progress and tend to regress concomitantly.
Cavernous Hemangioma of Liver. Four histologic types of hemangioma have been identified. A RICH will start to shrink right after the baby is born.
This type is much less common than IH. Results Of 472 hemangiomas 327 patients 339 72 were localized 84 18 were segmental 37 8 were indeterminate and 12 3 were multifocal 8 or more noncontiguous lesions. A congenital hemangioma hem-an-gee-o-ma is a vascular lesion that is present and fully grown at birth.
Congenital hemangiomas are usually divided into two groups. Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma RICH and non-involuting congenital hemangioma NICH. Some hemangiomas disappear over time and this is called regression.
There are many types of hemangiomas and they can occur throughout the body including in skin muscle bone and internal organs. These features allow to separate vertebral hemangiomas from bone lymphangiomas from true neoplastic vascular tumours such as hemangioendotheliomas hemangiopericytomas angiosarcomas from hemangioblastomas and from arteriovenous malformations with shunt. Doctors may diagnose a congenital hemangioma on a prenatal ultrasound.
Microscopic histologic description Two types. Of the blood vessels called hemangiomas may occur in the lids and give rise to soft bluish swellings. There are three main types of hemangioma.
This review highlights the key features of previously reported cases and discusses the differential diagnosis. Subtypes were correlated with race and ethnicity the incidence of complications and overall outcome. Most hemangiomas are infantile hemangiomas.
A hemangioma is a benign noncancerous tumor made up of blood vessels. The most common hemangioma of the lumbar spine and a hemangioma of the thoracic. A congenital hemangioma can shrink on its own rapidly involuting or RICH or be nonshrinking noninvoluting or NICH.
Often they disappear spontaneously but they. A hemangioma is a common vascular birthmark made of extra blood vessels in the skin. Cavernous hemangioma is the most common primary hepatic tumor.
It is more common in females FM 51 in whom it may rapidly increase in size during pregnancy or with estrogen therapy. For cervical this pathology is even more dangerous. But the main division into more and less dangerous conditions classification according to the degree of aggressiveness.
1 2 According to the ISSVA classification hemangiomas are classified into infantile hemangiomas IH. This neurocutaneous syndrome is the most frequent one and it is associated with several types of vascular and non-vascular abnormalities which can involve any organ of the body.
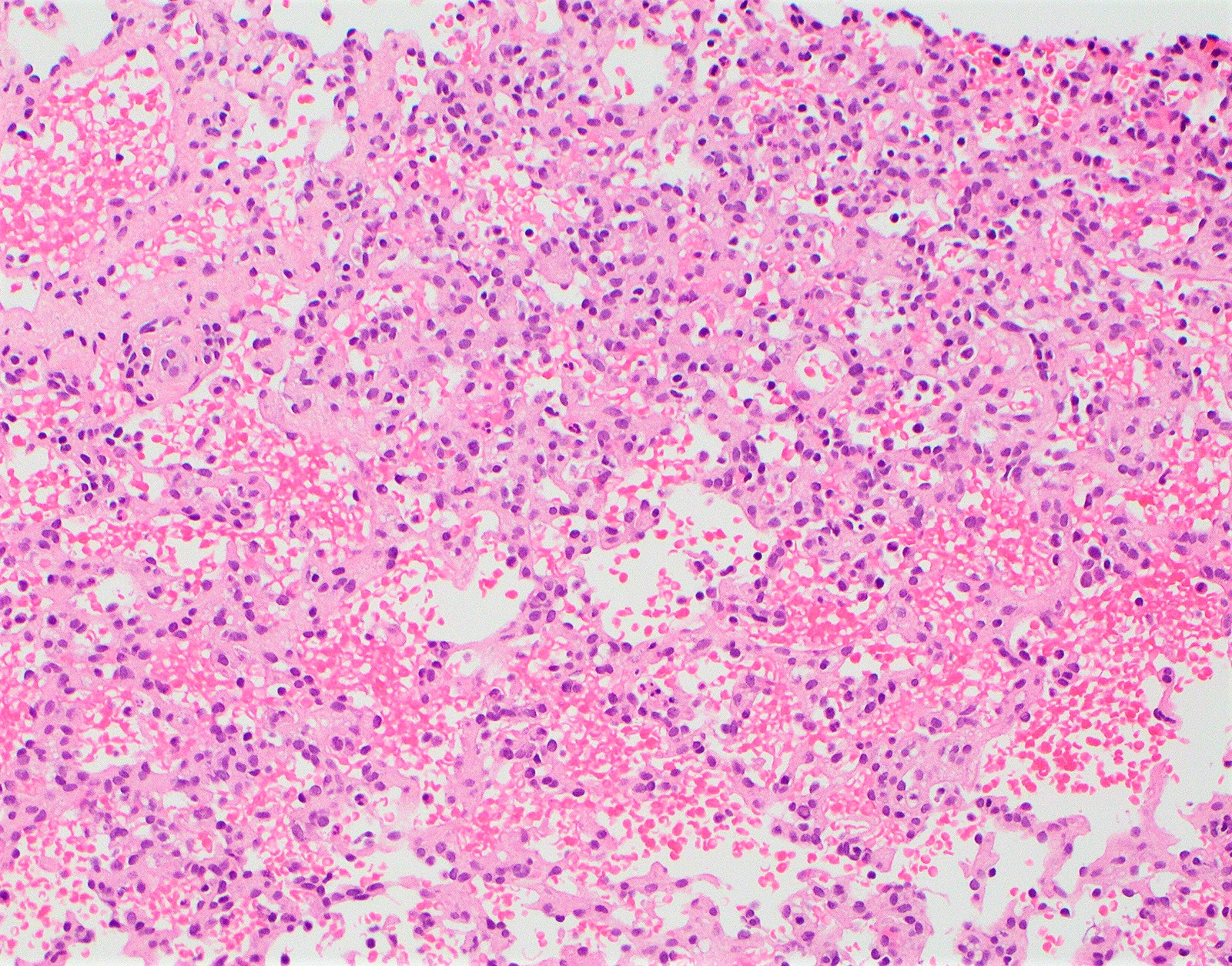
Pathology Of Infantile Hemangioma Juvenile Hemangioma Cellular Hemangioma Of Infancy Dr Sampurna Roy Md
 Lobular Capillary Hemangioma Mypathologyreport Ca
Lobular Capillary Hemangioma Mypathologyreport Ca
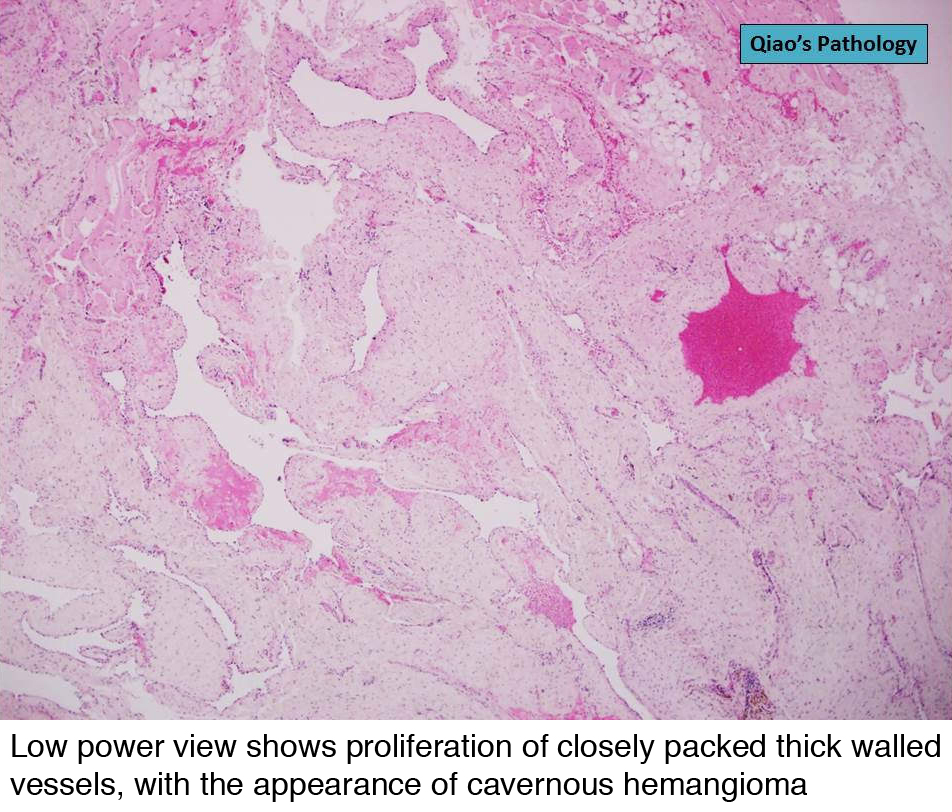 Pathology Outlines Venous Hemangioma
Pathology Outlines Venous Hemangioma
Hemangioma Portnotes Orthopaedicsone
Capillary Hemangioma Pathology Made Simple
Cavernous Hemangioma Pathology Made Simple
 Pyogenic Granuloma Lobular Capillary Hemangioma Histopathology Image 2 Path Quiz Case 70 Pathology Quiz Pathology Medical Science Anatomy And Physiology
Pyogenic Granuloma Lobular Capillary Hemangioma Histopathology Image 2 Path Quiz Case 70 Pathology Quiz Pathology Medical Science Anatomy And Physiology
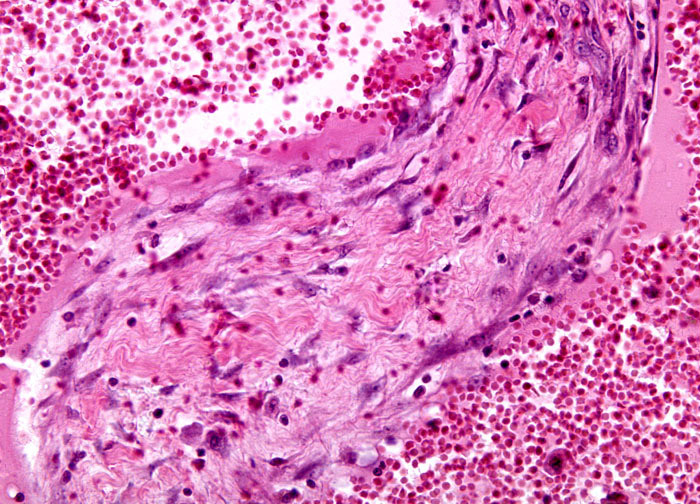 Cavernous Hemangioma At 20x Magnification Nikon S Microscopyu
Cavernous Hemangioma At 20x Magnification Nikon S Microscopyu
Cavernous Hemangioma Pathology Made Simple
 Histology A Cutaneous Hemangioma B Epithelioid Download Scientific Diagram
Histology A Cutaneous Hemangioma B Epithelioid Download Scientific Diagram
 Histology Of Mixed Cavernous And Capillary Angioma A Shows Cavernous Download Scientific Diagram
Histology Of Mixed Cavernous And Capillary Angioma A Shows Cavernous Download Scientific Diagram